tests for testicular torsion|testicular torsion prognosis : agency A history and physical exam consistent with testicular torsion mandates an immediate surgical consult for scrotal exploration. If history and physical exam suggest .
Resultado da 17 de jul. de 2020 · 幽浮2/xcom2 新手向攻略 防劝退指南. 22.5万 380 2020-07-17 19:59:45. 4236. 658. 630. 308. 前几天夏促入的幽浮2/xcom2,当时看b站上新手攻略不多,这游戏又挺容易劝退新手,所以自己玩了一会觉得很好玩就打算录个新手攻略,简单过了一下剧情和教程,后面再提了几个比较 .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Magrin_fxp7🕊️. O REI DOS VIDEOS VAZADOS 🥋. Morena Sub 16. Japa Nordestina. Ayarla Souza. Mc Mirella. Novinha No Banho. Novinha Sub 14. Menina Sub 13.
Testicular torsion is a clinical diagnosis, and patients typically present with severe acute unilateral scrotal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Physical examination may reveal a high-riding. Testicular torsion is a time-dependent diagnosis, a true urologic emergency, and early evaluation can assist in urologic intervention to prevent testicular loss. Ultrasound is the .
Testicular torsion is a twisting of the spermatic cord and its contents and is a surgical emergency affecting 3.8 per 100,000 males younger than 18 years annually. It accounts for .Testicular torsion is an emergency condition due to rotation of the testis and consequent strangulation of its blood supply. Symptoms are acute scrotal pain and swelling, nausea, and vomiting. Diagnosis is based on physical . Testicular torsion occurs when the testicle rotates on the spermatic cord, which brings blood to the testicle from the abdomen. If the testicle rotates several times, blood flow . A history and physical exam consistent with testicular torsion mandates an immediate surgical consult for scrotal exploration. If history and physical exam suggest .
Individual clinical findings that best predict testicular torsion include nausea and vomiting, past trauma, a tender testicle, an abnormal testicular lie (i.e., elevated or transverse), and.
Ultrasonography. Doctors may diagnose the condition based on a description of the symptoms and the physical examination findings. Alternatively, doctors may use imaging, usually ultrasonography, for diagnosis. Treatment of Testicular . Testicular torsion occurs when a testis torts on the spermatic cord resulting in the cutting off of blood supply. The most common symptom is acute testicular pain and the most common underlying cause, a bell-clapper deformity. The diagnosis is often made clinically but if it is in doubt, an ultrasound is helpful in confirming the diagnosis. .
American Urological Association Curriculum on Acute Scrotum: This case-study offering from the association's medical school curriculum covers the differential diagnosis of acute scrotum with a concentration on 6 conditions: epididymitis, .
Testicular torsion refers to the torsion of the spermatic cord structures and subsequent loss of the blood supply to the ipsilateral testicle. This is a urological emergency; early diagnosis and treatment are vital to saving the testicle and preserving future fertility. . Laboratory tests are unlikely to be of consequence, as no single test .
A diagnosis of testicular torsion should be suspected in any person presenting with acute scrotal pain and/or swelling, before other causes are considered.. Ask about:. Any scrotal pain — the location (including unilateral or bilateral), nature, radiation to surrounding structures, speed of onset, duration, severity, exacerbating factors (such as activity or positional changes). A history and physical exam consistent with testicular torsion mandates an immediate surgical consult for scrotal exploration. If history and physical exam suggest testicular torsion, immediate surgical consultation and exploration should take precedence over diagnostic tests. Usually affects young males but may affect males of any age.
How to treat testicular torsion. Testicular torsion is a medical emergency which requires immediate surgery (called an orchiopexy with detorsion) to restore blood flow to the testicles. Since it can take just four to six hours for permanent damage to set in, anyone concerned about testicular torsion should not wait.Testicular torsion is a twisting of the spermatic cord and its contents and is a surgical emergency affecting 3.8 per 100,000 males younger than 18 years annually. It accounts for 10% to 15% of
Testicular torsion, or twisted testicle, can be extremely painful. . A healthcare professional may also test the patient’s cremasteric reflex, which is highly effective in helping diagnose .Testicular torsion that goes on for more than a few hours can permanently damage the testicle, and a damaged testicle must be removed. . which probably won't happen if you have a testicular torsion. The doctor also might do tests to see if the spermatic cord is twisted, including: Ultrasound. High-frequency (Doppler) waves are used to make an .
Testicular torsion can occur at any age but commonly occurs soon after birth or between the ages of 12–18 years with a peak in incidence at age 13–14 years. . With regards to the intraoperative bleeding test, all patients with grade 3 bleeding (major bleeding that requires multiple hemoclips and sessions of hemocoagulation) required .↑ Blaivas, M, et al. Emergency evaluation of patients presenting with acute scrotum using bedside ultrasonography. Academic Emergency Medicine. 2001; 8(1):90-93. ↑ Barbosa, JA, et al. Development of initial validation of a scoring system to diagnose testicular torsion in children. The Journal of Urology. 2013; 189:1853-8. ↑ Gordon J, Rifenburg RP. . Spermatic Cord .Testicular torsion is the twisting of a testis on its spermatic cord so that the blood supply to the testis is blocked. Testicular torsion causes sudden, severe pain and later swelling of the affected testis. A doctor's examination and sometimes ultrasonography are needed for testicular torsion diagnosis. Treatment is to untwist the spermatic cord.
How common is testicular torsion? Testicular torsion occurs in teenage boys aged 13-18 years. This is found to happen in around 1 in 4,000 young men. Newborn babies and younger children sometimes develop this problem. It is uncommon over the age of 25 but does occur sometimes in older adults and can occur at any age.
Testicular torsion has an annual incidence of approximately 1 in 4,000 males younger than 25 years. 1 It is more common in children and adolescents, and delayed repair can result in the loss of . Investigations. The diagnosis of testicular torsion is a clinical one, therefore any suspected cases should be taken straight to theatre for scrotal exploration.. However, in cases with sufficient equipoise, Doppler ultrasound .
Each year, testicular torsion affects one in 4,000 males younger than 25 years. Early diagnosis and definitive management are the keys to avoid testicular loss. All prepubertal and young adult . A history and physical examination consistent with testicular torsion mandates an immediate surgical consult for scrotal exploration. If history and physical examination suggest testicular torsion, immediate surgical consultation and exploration should take precedence over diagnostic tests. Usually affects young males but may affect males of .
Testicular torsion refers to the torsion of the spermatic cord structures and subsequent loss of the blood supply to the ipsilateral testicle. . Menon VS, et al. Transscrotal Near Infrared Spectroscopy as a Diagnostic Test for Testis Torsion in Pediatric Acute Scrotum: A Prospective Comparison to Gold Standard Diagnostic Test Study. J Urol . Answer: Testicular torsion 1-15. Epidemiology. Bimodal incidence: 1 st year of life and teenage years . is the first-line imaging test recommended to rule in or out testicular torsion and should only be performed before surgical consult when patients with testicular pain have reassuring findings on history and exam.The recommendations on management of testicular torsion are based on the European Association of Urology (EAU) guideline Paediatric urology [Radmayr, 2021], the Royal College of Surgeons (RCS) joint publications Asymptomatic scrotal swelling, commissioning guide [] and Management of paediatric torsion, commissioning guide [], and expert opinion in review .
If history and physical exam suggest testicular torsion, immediate surgical consultation and exploration should take precedence over diagnostic tests. Intraoperative photograph showing extravaginal torsion of the spermatic cord and the necrotic testis in a newborn with discoloration of the right testicle at birthTesticular torsion in young boys and teen boys occurs when the testicles are not completely attached in the scrotum. This lets the testicles move more freely and twist. . He may also have tests, such as an ultrasound. This is a painless imaging test that uses sound waves to see the scrotum and testicles and check blood flow. Torsion of the testis is a surgical emergency. Although it occurs in all age groups, torsion is most common in adolescents. The typical presentation is with a tender, swollen scrotum and lower abdominal pain; symptoms are however variable and often much less marked in young children and neonates.
The cremasteric reflex has been reported to be absent in 100% of cases of testicular torsion, making it a potentially useful sign in this diagnosis. However, a significant number of case reports and small case series exist, demonstrating that the test is not 100% specific, and the reflex can be present in cases of testicular torsion. Testicular torsion is characterized by sudden-onset unilateral testicular pain, which may radiate to the lower abdomen, with nausea and vomiting. Clinical findings include a high-riding. testis. with an absent . cremasteric reflex. Imaging with .Testicular torsion is when the spermatic cord above your testicle twists, cutting off blood flow to your testicle. Testicular torsion can happen at any age, but it most often happens to boys ages 12 to 18 or babies. Without blood supply, the tissue of your testicle can die in a few hours . See a doctor right away if you think you have .Testicular torsion causes severe testicular pain and usually occurs in boys 10 years and older. While it generally occurs in adolescent boys, it may also occur during fetal development or shortly after a baby is born. Causes. In pre-adolescent and adolescent boys, torsion occurs primarily from incomplete attachment of the testes within the scrotum.
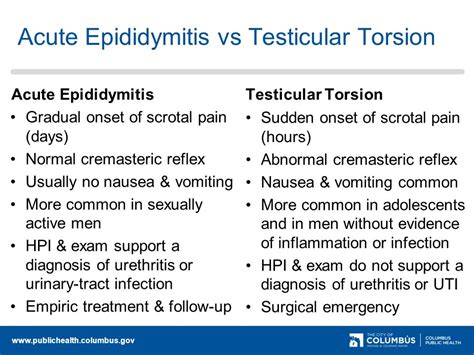
testicular torsion vs epididymitis signs
testicular torsion survival rate
WEB192.168.1.7 router login and password for your device at 192.168.1.7 We will help you get into your router or other devices on your network 192.168.1.7 is a private ip address used for local networks. You can login to the admin page by entering the 192.168.1.7 into your browser's address bar.
tests for testicular torsion|testicular torsion prognosis